A Deep Study the Aluminum Casting Process: From Layout to Finished Item
The light weight aluminum Casting procedure encompasses a number of vital stages, each calling for accuracy and knowledge. It starts with the style stage, where concepts advance right into detailed requirements. The preparation of mold and mildews complies with, utilizing different casting techniques. After melting and putting, the cooling phase identifies the last properties of the aluminum. Nevertheless, the journey doesn't end there; ending up procedures play a substantial role in achieving quality criteria. What takes place next in this complex procedure?
Recognizing Aluminum Casting
Aluminum Casting is an important procedure in producing that entails pouring molten light weight aluminum into a mold and mildew to create various forms and components. This technique is preferred for its capability to create detailed layouts with outstanding dimensional accuracy. The process begins with choosing high-quality aluminum alloys, which are after that melted at elevated temperatures. Once in a liquid state, the light weight aluminum is meticulously poured into mold and mildews, which can be made from sand, metal, or other products, relying on the wanted final product.
Air conditioning happens as the liquified light weight aluminum solidifies, forming the desired shape. After cooling down, the spreadings are gotten rid of from the molds and go through completing procedures such as machining or surface area treatment to improve their homes and look. Recognizing aluminum Casting not only highlights its importance in design and production yet additionally emphasizes its flexibility in creating light-weight, long lasting parts for various sectors, consisting of automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods.
The Style Process: From Idea to CAD
The style procedure for light weight aluminum Casting starts with first principle growth, where concepts are changed into concrete requirements. Following this phase, CAD modeling methods are used to develop specific electronic depictions of the styles. This shift from idea to CAD is necessary for making certain precision and usefulness in the Casting procedure.
Preliminary Concept Development
Initiating the layout procedure for aluminum Casting involves changing abstract concepts into substantial principles. This stage is fundamental, as it lays the groundwork for effective product development. Developers work together with designers and stakeholders to specify the practical requirements and visual components of the casting. Brainstorming sessions typically generate numerous ideas, which are then assessed for manufacturability, expediency, and cost-effectiveness. Sketches and initial versions might be developed to envision prospective styles. Comments from employee and clients is crucial in fine-tuning these concepts. Repetitive discussions assist to identify possible difficulties, ensuring that the last design straightens with both technical specs and user requirements. Ultimately, this stage sets the stage for the change from concept to even more comprehensive electronic representations.
CAD Modeling Techniques
As the layout process shifts from first concepts to in-depth depictions, CAD modeling methods come to be vital tools for designers and developers. These strategies allow for the development of specific, scalable digital versions that properly reflect the designated physical item. Usual methods include 3D solid modeling, surface area modeling, and parametric design, each offering distinct abilities for various task requirements. Engineers make use of software application like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and CATIA to fine-tune layouts, simulate performance, and identify prospective problems prior to manufacturing. The integration of CAD with other innovations, such as finite aspect evaluation (FEA), improves the layout procedure further by predicting material behavior under tension. Eventually, efficient CAD modeling simplifies interaction amongst staff member and enhances the general effectiveness of the light weight aluminum Casting procedure.
Preparing the Mold And Mildew: Sand, Die, and Investment Spreading
When preparing mold and mildews for light weight aluminum spreading, the selection of approach significantly affects the end product's quality and accuracy. Three key strategies are typically utilized: sand spreading, die casting, and financial investment spreading.
Sand Casting entails developing a mold and mildew from sand, which is affordable and flexible, making it ideal for complex geometries and large components. This technique, nevertheless, might produce a rougher surface coating contrasted to other strategies.
Pass away casting utilizes steel mold and mildews, making it possible for high-volume production and exceptional dimensional precision. This approach is optimal for generating detailed layouts with smooth surfaces and tight resistances yet needs higher upfront expenses due to mold and mildew construction.
Financial investment casting, also known as lost-wax spreading, offers phenomenal precision and surface area finish, making it ideal for elaborate parts. This technique entails producing a wax pattern, which is covered in ceramic, permitting great detail throughout the Casting process. Each method has its benefits, impacting the casting's characteristics and applications.
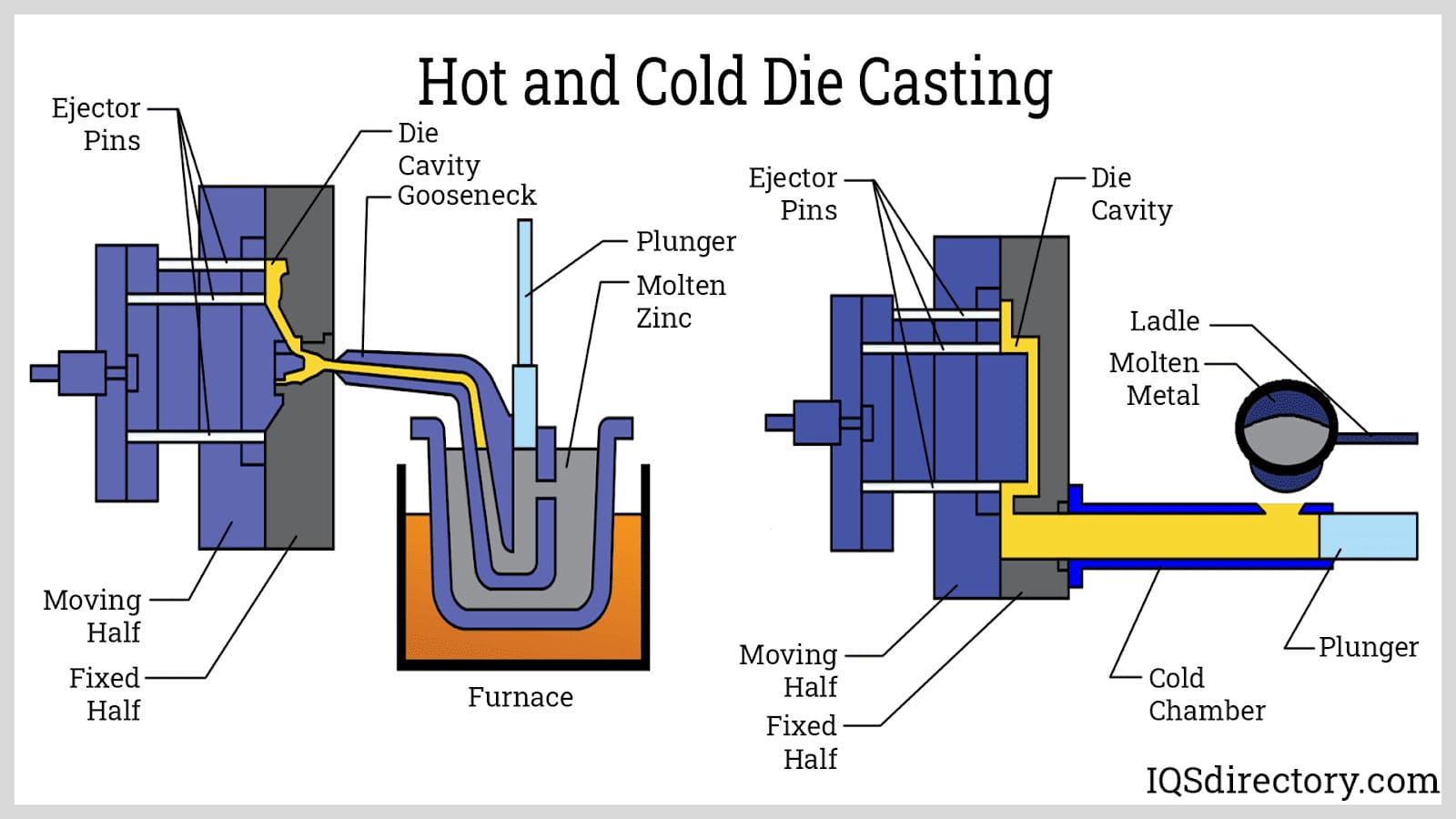
Thawing and Pouring Light weight aluminum: Methods and Tools
In the aluminum Casting process, reliable melting and pouring methods are critical for accomplishing premium outcomes. Various melting techniques and specialized putting equipment play a considerable duty in making sure perfect fluidness and temperature level control - Aluminum Casting Manufacturer. Understanding these fundamentals is critical for both beginner and knowledgeable shop specialists
Thawing Strategies Overview
A range of melting methods are used in the light weight aluminum Casting procedure, each customized to specific applications and manufacturing ranges. Usual methods include crucible melting, where aluminum is heated in a ceramic or metal container, commonly ideal for tiny sets. Induction melting utilizes magnetic fields to heat aluminum swiftly and effectively, perfect for larger production requirements. Electric arc heating systems provide a high-temperature setting, making them appropriate for reusing light weight aluminum scrap. In addition, rotating heating systems use a constant melting process, enhancing productivity. Each technique has its advantages, such as power i was reading this performance, thawing rate, and material quality, guaranteeing that makers can choose the most appropriate approach based upon their operational requirements and desired end results in the Casting procedure.
Putting Equipment Essentials
Adhering to the melting process, effective pouring tools plays a considerable duty in ensuring the successful transfer of liquified aluminum right into molds. Key parts consist of ladles, pouring mugs, and automated putting makers. Ladles, usually made of heat-resistant materials, are made to hold and deliver molten light weight aluminum safely. Putting mugs improve control during the transfer, assisting in a steady pour to minimize turbulence and oxidation. Automated pouring machines are significantly preferred, ensuring regular flow prices and reducing human error. These equipments can be programmed for precision, maximizing casting quality. Furthermore, temperature level monitoring gadgets are vital to ensure the liquified aluminum stays within the ideal temperature variety, more boosting the quality of the final actors item. Correct selection and maintenance of pouring devices are essential for efficiency and security.
Cooling and Solidification: Transforming Fluid to Solid
Air conditioning and solidification play a crucial duty in the aluminum Casting procedure, as they figure out the final residential properties of the cast steel. After putting, the molten light weight aluminum begins to shed warm, shifting from fluid to strong. This cooling phase is crucial, as it affects mechanical residential or commercial properties such as toughness, microstructure, and ductility. The rate of air conditioning can vary based upon elements such as mold and mildew material, density, and environmental problems. Rapid air conditioning might lead to a finer grain framework, enhancing toughness, while slower cooling can bring about coarser grains, affecting ductility.
In addition, uniform air conditioning is essential to stop problems such as warping or fracturing. As the metal solidifies, the development of dendrites occurs, which are tree-like frameworks that influence the overall stability of the spreading. Comprehending the air conditioning and solidification dynamics enables designers and foundry workers to enhance the procedure, guaranteeing that the last product satisfies the essential specifications and high quality criteria.

Finishing Processes: Machining, Layer, and Examination
Finishing processes are critical in refining light weight aluminum castings to fulfill rigorous specs and enhance efficiency. These procedures normally include coating, machining, and examination, each playing an important role in accomplishing the wanted top quality.
Machining includes getting rid of excess material from the Casting to acquire exact measurements and surface coatings. Techniques such as milling, transforming, and grinding are commonly utilized to assure that the end product meets layout tolerances.
Finishing offers to safeguard the light weight aluminum surface from environmental variables, enhancing corrosion resistance and aesthetic allure. Options include anodizing, powder layer, and painting, each offering unique benefits relying on the application.
Inspection is vital to verify that the finished castings satisfy quality standards. Methods such as aesthetic assessment, dimensional checks, and non-destructive screening are used to identify any problems. With each other, these completing processes ensure that aluminum spreadings are reliable, resilient, and prepared for their designated applications.
Applications of Light Weight Aluminum Castings in Numerous Industries

Additionally, the customer items industry integrates aluminum castings in items like cookware and home appliances, exploiting on their thermal conductivity and sturdiness. The building and construction industry employs aluminum castings in window structures, doors, and attractive elements, enhancing looks while keeping functionality. Additionally, the marine market relies upon light weight aluminum spreadings for watercraft components, where resistance to saltwater corrosion is important. In general, aluminum castings supply ingenious options throughout numerous applications, making them indispensable in modern manufacturing procedures.
Regularly Asked Inquiries
What Are the Ecological Influences of Light Weight Aluminum Casting?
The environmental effects of aluminum Casting include energy-intensive manufacturing, greenhouse gas exhausts, and possible water air pollution. In addition, mining bauxite for aluminum adds to habitat destruction, while reusing initiatives can minimize some adverse impacts.
Exactly How Does Aluminum Casting Compare to Various Other Metal Casting Processes?
Aluminum casting generally supplies benefits like light-weight buildings and rust resistance contrasted to various other metal Casting processes. It might have restrictions in stamina and temperature resistance, making its viability dependent on details application demands.
What Safety Preventative Measures Are Required During Light Weight Aluminum Casting?
Throughout aluminum spreading, safety preventative measures include putting on protective equipment, guaranteeing correct ventilation, keeping devices, and following stringent protocols to manage liquified metal. These actions aim to decrease dangers such as burns, breathing of fumes, and equipment breakdowns.
Can Aluminum Castings Be Recycled After Use?
Light weight aluminum castings can without a doubt be recycled after usage. The recycling process maintains the material's buildings, making it a sustainable choice. This technique considerably lowers waste and conserves power, advertising environmental obligation in making industries.
What Are Typical Issues in Aluminum Castings and Their Causes?
Typical issues in aluminum castings include porosity, cool shuts, and shrinking - Aluminum Casting Manufacturer. These problems commonly occur from insufficient melting temperatures, incorrect mold design, and insufficient air conditioning rates, affecting the overall high quality and performance of the final item
Aluminum Casting is an essential procedure in manufacturing that involves pouring molten aluminum into a mold to produce different shapes and elements. The design process for aluminum Casting begins with initial idea development, where ideas are transformed into tangible specifications. Initiating the design process for aluminum Casting entails changing abstract concepts right into concrete ideas. In the aluminum Casting process, effective melting and putting strategies are critical for achieving top quality results. A variety of melting strategies are used in the light weight aluminum Casting process, each tailored to specific applications and production ranges.